2017年國民經濟和社會發展計劃報告(全文)
Full text: Report on China's economic, social development plan (2017)
| 3月5日,第十二屆全國人民代表大會第五次會議在北京人民大會堂開幕。 [新華社] The fifth session of the 12th National People's Congress opens at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing, capital of China, March 5, 2017. [Photo/Xinhua] |
關于2016年國民經濟和社會發展計劃執行情況與2017年國民經濟和社會發展計劃草案的報告 | Report on the Implementation of the 2016 Plan for National Economic and Social Development and on the 2017 Draft Plan for National Economic and Social Development |
——2017年3月5日在第十二屆全國人民代表大會第五次會議上 | Delivered at the Fifth Session of the Twelfth National People's Congress on March 5, 2017 |
國家發展和改革委員會 | National Development and Reform Commission |
| 各位代表: | Esteemed Deputies, |
| 受國務院委托,現將2016年國民經濟和社會發展計劃執行情況與2017年國民經濟和社會發展計劃草案提請十二屆全國人大五次會議審議,并請全國政協各位委員提出意見。 | The National Development and Reform Commission has been entrusted by the State Council to submit this report on the implementation of the 2016 plan and on the 2017 draft plan for national economic and social development to the Fifth Session of the Twelfth National People's Congress (NPC) for your deliberation and for comments from the members of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC). |
| 一、2016年國民經濟和社會發展計劃執行情況 | I. Implementation of the 2016 Plan for National Economic and Social Development |
| 去年以來,國內外環境復雜嚴峻,世界經濟艱難復蘇,國內經濟下行壓力依然較大。在以習近平同志為核心的黨中央堅強領導下,各地區各部門堅持穩中求進工作總基調,堅持新發展理念,認真執行十二屆全國人大四次會議審議批準的2016年國民經濟和社會發展計劃,落實全國人大財政經濟委員會的審查意見,以推進供給側結構性改革為主線,適度擴大總需求,堅定推進改革,妥善應對風險挑戰,引導形成良好社會預期,扎實做好各項工作,經濟社會保持平穩健康發展,“十三五”實現良好開局,計劃執行情況總體是好的。 | Last year, conditions both at home and abroad were complex and challenging; the global economic recovery struggled to take effect while downward pressure on China's economy remained significant. However, under the firm leadership of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) with Comrade Xi Jinping at its core, all regions and departments continued to follow the general principle of making progress while keeping performance stable, upheld the new development philosophy, earnestly implemented the 2016 plan approved at the Fourth Session of the Twelfth NPC, and acted in line with the review of the plan by the NPC's Financial and Economic Affairs Committee. In accordance with the keynote of advancing supply-side structural reform, we appropriately increased aggregate demand, advanced reform with determination, responded effectively to risks and challenges, guided public expectations to ensure they remained positive, and worked hard to deliver a good performance in all areas of work. As a result, economic and social development remained stable and healthy, the 13th Five-Year Plan got off to a good start, and implementation of the 2016 Plan for National Economic and Social Development was successful overall. |
| (一)創新和加強宏觀調控,經濟運行保持在合理區間。在區間調控基礎上,加強定向調控、相機調控,積極的財政政策力度加大,穩健的貨幣政策靈活適度,確保經濟平穩運行。國內生產總值達到74.41萬億元,增長6.7%,符合預期。 | 1. We developed new and better ways of conducting macro regulation to keep the economy operating within an appropriate range. On the basis of range-based regulation, we strengthened targeted and well-timed regulation and pursued a more proactive fiscal policy as well as a prudent monetary policy that retained an appropriate degree of flexibility so as to ensure that economic performance was stable. China's gross domestic product (GDP) rose to 74.41 trillion yuan, an increase of 6.7%, meeting our projected target. |
圖表1:2016年各季度國內生產總值和經濟增長率 新華社發 | Figure 1. Quarterly GDP and Growth Rate in 2016 |
| 一是消費基礎作用進一步增強。促進消費帶動轉型升級的行動方案出臺,“十大擴消費行動”全面推進。促進綠色消費、實體零售創新轉型、交通物流融合發展的政策出臺實施。進一步擴大旅游文化體育健康養老教育培訓等領域消費的意見發布實施,服務消費蓬勃興起,汽車等實物消費擴大升級。激發重點群體活力帶動城鄉居民增收的實施意見出臺,居民消費能力持續提升。社會消費品零售總額增長10.4%。消費在經濟增長中發揮主要拉動作用,貢獻率達到64.6%,消費和投資的比例關系進一步改善。 | 1) Consumption played a more fundamental role. The action plan to stimulate industrial transformation and upgrading through increased consumption was formulated, and the Ten Initiatives for Boosting Consumer Spending were implemented. We implemented the policies for promoting green consumption, transformation of physical retail businesses through innovation, and integrated development of transportation and logistics. The guidelines on further boosting consumer spending in tourism, culture, sports, health, elderly care, education, and training services were promulgated and implemented; the consumption of services flourished; and consumer spending on automobiles and other physical goods was increased and upgraded. We formulated the guidelines on providing incentives to key groups to promote an overall increase in urban and rural incomes, and people's ability to consume continued to increase. Total retail sales of consumer goods for the year rose by 10.4%. Consumption served as a major driver of economic growth, making a 64.6% contribution. And there was a further improvement in the ratio between consumption and investment. |
專欄1:十大擴消費行動 新華社發 | Box 1: Ten Initiatives for Boosting Consumer Spending |
| 二是投資保持穩定增長。圍繞補短板、調結構、增供給,努力擴大合理有效投資。中央預算內投資結構繼續優化,政府投資項目儲備庫和三年滾動投資計劃初步形成,重大工程建設加快推進。著力調動民間投資積極性,制定促進民間投資“26條”政策,加大政府和社會資本合作(PPP)模式推廣力度。全社會固定資產投資增長7.9%,民間投資占固定資產投資(不含農戶)比重為61.2%。 | 2) Investment sustained steady growth. Strengthening areas of weakness, making structural adjustment, and increasing supply were our primary focus in working to increase rational and effective investment. We further improved the structure of investments falling within the central government budget, took initial steps to set up the reserve of government investment projects and formulate the three-year rolling investment plan, and stepped up the construction of major projects. We channeled great energy into stimulating private investment, formulated a 26-point policy to ensure its sound development, and worked to expand the application of public-private partnership (PPP) models. Total fixed-asset investment for the year rose by 7.9%, of which 61.2% came from nongovernmental sources (excluding rural households). |
專欄2:促進民間投資健康發展 新華社發 | Box 2: Measures for Encouraging Sound Development of Private Investment |
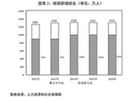
| 三是就業形勢總體較好。基層就業社保服務設施和公共實訓基地建設加快推進,高校畢業生和化解過剩產能職工就業服務工作力度加大,支持農民工等人員返鄉創業試點持續推進。全年城鎮新增就業1314萬人,年末城鎮登記失業率4.02%。 | 3) The overall employment situation remained positive. We sped up efforts to develop community-level facilities providing employment and social security services and to establish public vocational training centers, provided better services to college graduates as well as to workers laid off due to the scaling-down of overcapacity, and continued to advance pilot projects to support rural migrant workers returning home to set up businesses. An additional 13.14 million urban jobs were created over the year, and the registered urban unemployment rate stood at 4.02% at the end of 2016. |
圖表2:城鎮新增就業 新華社發 | Figure 2. Urban Jobs Created |
| 四是價格總水平基本穩定。大宗商品價格調控進一步強化,生豬價格調控有效開展,汛期、重點節假日蔬菜等重要商品價格監測預警和調控監管加強。價格監管和反壟斷執法強力推進,先后查處了數起反壟斷案件。全年居民消費價格上漲2.0%。 | 4) Overall prices were generally stable. We increased regulation over commodity prices, effectively carried out regulation over the price of hogs, and strengthened monitoring, early warning, regulation, and oversight over the prices of major commodities such as vegetables during the flood season and major holidays. Oversight over pricing was tightened up and law enforcement efforts to counter monopolistic pricing intensified with numerous cases being investigated and dealt with. The consumer price index (CPI) for the year rose by 2.0%. |
| 五是各類風險挑戰得到妥善應對。加強對外投資活動真實性審查,引導對外投資健康有序發展。按照市場化、法治化原則防范化解債券違約風險。因城因地施策,分類調控房地產市場。防范應對部分地區特別是長江流域發生的嚴重洪澇等災害,及時有力開展搶險救災,最大限度降低了災害損失,恢復重建有序進行。 | 5) Risks and challenges were handled appropriately. We stepped up reviews to verify the authenticity of outbound investment projects and worked to ensure the sound and orderly development of overall outbound investment. We employed market-oriented, law-based measures to guard against and defuse bond default risks. Policies tailored to local conditions were implemented to regulate the real estate market on a per-category basis. We worked to guard against and deal with severe flooding in some regions, particularly the Yangtze basin, as well as other natural disasters, and acted quickly to provide effective rescue and relief so as to minimize damage, and ensure recovery and reconstruction efforts proceeded in an orderly manner. |
| (二)扎實推進供給側結構性改革,“三去一降一補”五大重點任務初見成效。加強政策引導和支持,建立工作推進機制,去產能、去庫存、去杠桿、降成本、補短板取得初步成效。 | 2. We worked to secure solid progress in supply-side structural reform,achieving initial success in the five priority tasks of cutting overcapacity, reducing excess inventory, deleveraging, lowering costs, and strengthening points of weakness. By enhancing policy guidance and support and establishing an effective work mechanism, we achieved preliminary progress in our efforts to carry out the five priority tasks. |
| 一是去產能年度任務提前超額完成。《國務院關于鋼鐵行業化解過剩產能實現脫困發展的意見》(國發〔2016〕6號)和《國務院關于煤炭行業化解過剩產能實現脫困發展的意見》(國發〔2016〕7號)印發實施。組織開展了淘汰落后、違法違規建設項目清理、聯合執法三個專項行動,嚴格控制新增產能,加快淘汰落后產能,有序引導過剩產能退出。積極做好職工安置和債務處置,推進企業兼并重組、轉型升級和布局優化。及時妥善應對供需調整、價格波動影響。2016年退出鋼鐵和煤炭產能分別超過6500萬噸和2.9億噸,超額完成年度目標任務。鋼鐵、煤炭企業效益轉好,拖欠減少,現金流緊張、安全投入欠賬、工資欠發緩發等問題得到一定緩解,行業運行狀況和市場預期有所改善。 | 1) Annual targets for cutting overcapacity were met ahead of schedule and were surpassed. The State Council's Guidelines on Addressing Overcapacity and Achieving a Turnaround in the Steel Industry (G.F. [2016] No. 6) and the State Council's Guidelines on Addressing Overcapacity and Achieving a Turnaround in the Coal Industry (G.F. [2016] No. 7) were published and implemented. We launched three initiatives which focused on shutting down outdated production facilities, dealing with projects that violated laws and regulations, and carrying out coordinated law enforcement, thereby strictly controlling the expansion of production capacity, ensuring the shutting down of outdated production facilities was accelerated, and guiding the orderly elimination of overcapacity. We made appropriate arrangements to ensure that laid-off employees were resettled and provided employment and that enterprise debts were properly handled; and we encouraged businesses affected by overcapacity to merge, restructure, transform, and upgrade, or optimize business distribution. We took timely and appropriate action in responding to the effects of adjustments in supply and demand and price fluctuations. In 2016, we reduced excess production capacity by over 65 million metric tons of steel and over 290 million metric tons of coal; both numbers surpassed the targets for the year. The steel and coal industries operated more efficiently: cases of companies being in arrears were reduced, cash-flow problems were eased, and problems of insufficient investment in workplace safety, overdue wages, and outstanding payments were alleviated to some extent. Overall, the performance of both industries as well as market expectations improved. |
| 二是去庫存加快推進。推動農業轉移人口落戶城鎮,滿足新市民住房需求,年末商品住宅待售面積比上年末減少4991萬平方米。棚戶區住房改造貨幣化安置比例進一步提高,全年貨幣化安置294萬戶,占全年棚改開工量的48.5%,比2015年提高18.6個百分點。 | 2) Work to cut excess inventory surged ahead. We promoted the granting of urban residency to people who have moved to cities from rural areas and worked to ensure the housing needs of new urban residents were met, such that by the end of 2016, the area of commodity housing for sale was 49.91 million square meters less than it was at the end of 2015. We further expanded the use of direct monetary housing compensation for people displaced by the rebuilding of run-down urban areas. 2.94 million households received monetary housing compensation over the year, accounting for 48.5% of the year's newly-commenced projects to rebuild run-down urban areas; this marked an increase of 18.6 percentage points over 2015. |
| 三是去杠桿成效初步顯現。《國務院關于積極穩妥降低企業杠桿率的意見》(國發〔2016〕54號)印發實施。采取兼并重組、市場化法治化債轉股、發展股權融資等綜合性措施,積極穩妥降低企業杠桿率。啟動市場化銀行債權轉股權,截至2016年底,多家商業銀行通過實施機構共選擇了資產負債率偏高但具有發展前景的行業龍頭企業20家,自主協商達成債轉股框架協議,協議金額超過2500億元。2016年末,全國規模以上工業企業資產負債率55.8%,同比下降0.4個百分點。 | 3) Efforts to deleverage delivered initial results. The State Council's Guidelines on Proactively yet Prudently Lowering Enterprise Leverage Ratios (G.F. [2016] No. 54) were published and implemented. We encouraged business mergers and restructuring, promoted market-oriented and law-based debt-for-equity swaps, developed equity financing, and adopted other comprehensive measures so as to reduce business leverage ratios in an active yet prudent way. We launched an initiative for enterprises to engage in market-based debt-for-equity swaps with banks. By the end of 2016, a number of commercial banks had selected, via relevant agencies, 20 leading enterprises, which, despite having relatively high debt-to-asset ratios, had good prospects for development. Framework agreements on debt-for-equity swaps were drawn up with these enterprises on the basis of independent consultation, and are worth over 250 billion yuan. At the end of 2016, the debt-to-asset ratio of nationwide industrial enterprises with annual revenue from their main business operations of 20 million yuan or more was 55.8%, a year-on-year decrease of 0.4 percentage point. |
| 四是降成本取得明顯成效。《國務院關于印發降低實體經濟企業成本工作方案的通知》(國發〔2016〕48號)印發實施。持續推進簡政放權放管結合優化服務改革,降低制度性交易成本。全面推開營改增試點,階段性降低“五險一金”繳費比例。實施煤電價格聯動,推進輸配電價改革,擴大電力直接交易規模,完善基本電價執行方式,降低企業用能成本。清理規范進出口環節、金融等領域涉企收費,推進鐵路貨運體制改革,開展物流業降本增效專項行動,印發實施推進物流大通道建設行動計劃。2016年,規模以上工業企業每百元主營業務收入中的成本同比降低0.1元,利潤率同比提高0.19個百分點。 | 4) Significant progress was achieved in reducing costs. The State Council's Circular on Publishing the Work Plan on Reducing the Costs of Enterprises in the Real Economy (G.F. [2016] No. 48) was published and implemented. We continued to promote the reforms to streamline administration, delegate more powers, improve regulation, and provide better services, thereby reducing transaction costs imposed by government. We extended trials of replacing business tax with value added tax (VAT) to all sectors and appropriately lowered the ratio of enterprise contributions for old-age insurance, medical insurance, unemployment insurance, workers' compensation, maternity insurance, and housing provident fund schemes for the current stage. We implemented the mechanism for coupling the price of coal with that of electricity, promoted price reform of electricity transmission and distribution, increased the number of direct sales by electricity generation companies to users, and improved the implementation of the basic electricity pricing scheme, so as to lower enterprise energy costs. We reviewed and standardized fees and charges levied on enterprises related to imports and exports and financial services, pushed forward in reforming the freight transportation system for railways, launched a cost-reduction and performance-improvement campaign within the logistics industry, and published and implemented an action plan to develop logistics channels. In 2016, industrial enterprises with annual revenue from their main business operations of 20 million yuan or more reduced their costs by 0.1 yuan per 100 yuan of income from their main business operations and increased their profit rate by 0.19 percentage point on a year-on-year basis. |
圖表3:降低實體經濟企業成本 新華社發 | Figure 3. Lowering Business Costs in the Real Economy |
| 五是補短板力度加大。堅持既利當前又利長遠,既重硬設施又重軟能力,以市場化投融資方式帶動銀行貸款等資金投放,在脫貧攻堅、災后水利恢復重建、社會事業、創新能力、新產業等關鍵領域和薄弱環節,抓好補短板建設。全年完成1000萬以上農村貧困人口脫貧目標任務。 | 5) Efforts to strengthen points of weakness were intensified. Keeping in mind the need to secure both short-term and long-term benefits and focusing on the development of both infrastructure and management and services, we pursued market-based investment and financing initiatives to stimulate bank loans and other forms of investment and worked to strengthen points of weakness in the key areas of poverty alleviation, post-disaster water conservancy restoration and reconstruction, social programs, innovation capacity-building, new industry, and other areas in need of attention. We achieved our target of helping more than 10 million rural residents lift themselves out of poverty over the course of the year. |
| (三)改革開放取得新突破,經濟社會發展活力進一步釋放。一批具有標志性、關鍵性的重大改革方案出臺實施,重要領域和關鍵環節改革取得突破性進展,開放型經濟發展水平不斷提升。 | 3. We made new breakthroughs in reform and opening up, unleashing new impetus for economic and social development. We launched a number of crucial signature reform plans, made breakthroughs in reform of major areas and key sectors, and improved the performance of China's open economy. |
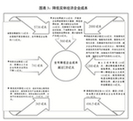
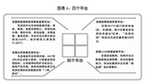
| 一是簡政放權放管結合優化服務改革向縱深推進。在提前完成本屆政府減少行政審批事項三分之一目標的基礎上,去年又取消165項國務院部門及其指定地方實施的審批事項,清理規范192項審批中介服務事項、220項職業資格許可認定事項。第三次修訂政府核準的投資項目目錄。商事制度改革繼續深化。全面推行“雙隨機、一公開”,增強事中事后監管的有效性,推進“互聯網+政務服務”。市場準入負面清單制度改革試點開局良好。“放管服”四大平臺建成運行。 | 1) Reforms to streamline administration, delegate more powers, improve regulation, and provide better services were intensified. The goal of the current administration to cut the number of items requiring government review by a third had been achieved ahead of schedule. On that basis, last year we cancelled the requirement on a further 165 items for review by State Council departments and authorized local governments. We also overhauled and standardized 192 items of intermediary services for government review as well as 220 items of approvals and accreditations for professional qualifications. The Catalog of Investment Projects Requiring Government Review was revised for the third time. Reform of the business system was deepened. We fully implemented the oversight model consisting of inspections of randomly selected entities by randomly selected inspectors and the public release of inspection results, made operational and post-operational oversight more effective, and promoted the Internet Plus government services model. The newly-launched reform piloting a negative list for market access yielded positive results. The four major platforms for streamlining administration, delegating more powers, improving regulation, and providing better services have all been assembled and are in operation. |
專欄3:“放管服”改革 新華社發 | Box 3: Reforms to Streamline Administration, Delegate More Powers, Improve Regulation, and Provide Better Services |
圖表4:四個平臺 新華社發 | Figure 4. The Four Major Platforms |
| 二是投融資體制改革步伐加快。深化投融資體制改革意見、企業投資項目核準和備案管理條例出臺,新一輪投融資體制改革全面展開。修訂發布中央預算內投資補助和貼息項目管理辦法,制定80個專項管理辦法。濟青、杭紹臺等鐵路吸引社會資本示范項目取得積極進展。 | 2) Reform of the investment and financing systems picked up pace. Guidelines on deepening reform of the investment and financing systems and regulations on the review and reporting of investment projects for enterprises were introduced, spurring a new round of reform throughout the investment and financing systems. We revised regulations on the management of projects for which the central government budget provides investment and loan-interest subsidies, and formulated 80 specific documents concerning the management of such projects. Significant progress was made in demonstration initiatives to attract private capital for projects such as the Ji'nan-Qingdao and Hangzhou-Shaoxing-Taizhou railway lines. |
| 三是價格改革繼續深化。輸配電價改革試點實現所有省級電網全覆蓋。建立天然氣管道運輸定價新機制,占消費總量80%以上的非居民用氣門站價格主要由市場主導形成。石油天然氣交易市場加快發展。90%左右的城市已推廣居民階梯水電氣價。全面推進醫療服務價格改革。鐵路、民航旅客票價市場化程度明顯提高。農業水價綜合改革穩步推進。完善稻谷和小麥最低收購價政策,棉花、大豆目標價格改革試點深入推進。 | 3) Price reform was deepened. Trials to reform electricity transmission-and-distribution prices were extended to all provincial-level grids. We established a new pricing mechanism for the pipeline transportation of natural gas, and worked to ensure that the market decided citygate prices of natural gas for non-household users, who accounted for over 80% of natural-gas consumption. Markets for trading petroleum and natural gas experienced rapid development. Around 90% of cities have adopted tiered pricing for household water, electricity, and natural gas usage. Price reforms for medical services were implemented across the board and pricing for passenger rail and airline tickets became noticeably more market based. Comprehensive pricing reform on water for agricultural use registered solid progress. We improved the minimum state purchase price policy on rice and wheat and pressed on with pilot reforms for ensuring base prices for cotton and soybeans. |
專欄4:重點領域價格改革 新華社發 | Box 4: Price Reform in Key Areas |
| 四是國有企業和重點行業改革穩步開展。國企改革“1+N”文件體系基本形成,加快剝離辦社會職能和解決歷史遺留問題工作方案等配套文件出臺,深化國企改革九項重點任務、十項改革試點扎實推進。第一批混合所有制改革試點進入實施階段。第一批國有資本投資公司試點取得階段性進展。31個省(區、市)電改方案獲批復,公布了首批105個增量配電業務改革試點項目。各省(區、市)國有林場改革實施方案和內蒙古、吉林、黑龍江重點國有林區改革實施方案均已制定完成,浙江、湖南、江西等6省國有林場改革試點順利完成。鹽業體制改革方案出臺,全面放開食鹽出廠、批發和零售價格。改革玉米收儲制度,將東北地區玉米臨時收儲政策調整為市場化收購加補貼新機制。政策性糧食和儲備棉庫存消化進展順利。 | 4) Steady progress was made in the reform of State-owned Enterprises (SOEs) and major industries. In putting in place a framework that consists of the Guidelines on Deepening Reform of SOEs as well as supplementary documents, we promulgated work plans to more quickly relieve SOEs of their obligations to operate social programs and help them address other longstanding issues, and steadily pressed ahead with the nine major tasks for deepening SOE reform and the 10 pilot SOE reforms*. We implemented the pilot reform to introduce mixed ownership for an initial group of SOEs and made progress in the trials to establish the first group of state capital investment companies. We approved reform plans for the electricity industries in 31 provinces,autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government, and released the first batch of 105 trial projects to increase the number of electricity distributors. Plans were formulated for reforming state forestry farms in all provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government and for reforming key state forestry areas in Inner Mongolia, Jilin, and Heilongjiang. Trial reforms on state forestry farms were successfully concluded in Zhejiang, Hunan, Jiangxi, and three other provinces. The plan for structural reform of the salt industry was issued, and all controls on producer, wholesale, and retail prices of salt were lifted. The system for purchasing and stockpiling corn was reformed, and the policy for temporary purchase and storage of corn in the northeast was replaced with a mechanism based on market-price purchases and supplementary subsidies. The work to reduce stockpiles of grain and cotton through the provision of policy support proceeded smoothly. * They are to: ensure the power of the board of directors of SOEs; carry out competitive selection and employment of executives and managers; promote the professional management system; implement differentiated pay in SOEs; develop companies for state capital investment and operations; merge and reorganize central government enterprises; introduce mixed-ownership structures in some major sectors; allow employees of SOEs with mixed-ownership structures to hold shares in their employer company; make information on SOEs public; and relieve SOEs of their obligation to operate social programs and help them address any other longstanding issues. |
專欄5:國有企業改革 新華社發 | Box 5: Reform of SOEs |
| 五是公平競爭市場環境加快形成。印發完善產權保護制度依法保護產權的意見,依法平等保護各種所有制經濟權益。工業用地市場化配置改革試點穩步實施。在市場體系建設中建立公平競爭審查制度的意見出臺,從源頭上預防政府部門制定出臺限制競爭的政策措施。社會信用體系建設取得新進展,出臺政務、個人、電子商務領域誠信建設指導意見,50多個部門在12個領域開展失信聯合懲戒、3個領域開展守信聯合激勵。打擊侵權假冒合力增強,查辦違法犯罪案件17萬余件。國內貿易流通體制改革發展綜合試點穩步推進。 | 5) Work to create a fair and competitive market was accelerated. The guidelines on improving the property rights protection system and protecting property rights in accordance with the law were published so as to ensure the rights and interests of economic entities under all forms of ownership are subject to law-based protection on an equal footing. Steady progress was made in the pilot reform for market-based allocation of land designated for industrial purposes. Guidelines on establishing a review mechanism within the market system to ensure fair competition were issued so as to impose direct controls on government departments preventing them from adopting policies or measures that eliminate or stifle competition. New headway was made in developing a credit rating system, and guidelines on enhancing the credit standing of governments and individuals, and within the e-commerce sector, were formulated. More than 50 departments worked together in 12 sectors to take punitive actions against those who act in bad faith and in three sectors to provide incentives to those who act in good faith. Coordinated efforts to combat infringements and counterfeiting were enhanced, with over 170,000 cases of illegal and criminal activities being investigated and handled. Steady progress was achieved in the comprehensive trials to reform and develop the domestic commodity distribution system. ? |
| 六是財稅金融改革有序推進。《國務院關于推進中央與地方財政事權和支出責任劃分改革的指導意見》(國發〔2016〕49號)出臺實施。全面推開營改增試點,將建筑業、房地產業、金融業、生活服務業納入營改增范圍,并將所有企業新增不動產所含增值稅納入抵扣范圍。全面實施資源稅從價計征改革,開展水資源稅改革試點。深化國有商業銀行和開發性、政策性金融機構改革。存款保險制度平穩運行。上海自貿試驗區部分金融開放創新舉措推廣至廣東、天津、福建自貿試驗區。“深港通”開啟。 | 6) Fiscal, tax, and financial reforms proceeded in an orderly manner. The State Council's Guidelines on Advancing Reform for the Sharing of Fiscal Authority and Spending Responsibilities between the Central and Local Governments (G.F. [2016] No. 49) were promulgated and implemented. We extended trials to replace business tax with VAT to all sectors, including the construction, real estate, financial, and consumer service industries, and ensured that VAT deductions cover all new immovable property of enterprises. Ad valorem rates were introduced for all resource taxes, and trial reforms to levy a water-resource tax were carried out. Reform of state-owned commercial banks as well as of development and policy-backed financial institutions were deepened. The deposit insurance system performed solidly. A number of measures for financial-sector opening up and innovation created by the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone were replicated in the pilot free trade zones in Guangdong, Tianjin, and Fujian. The Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect was launched. |
| 七是社會領域改革加快推進。中央和國家機關公務用車制度改革全面完成,地方黨政機關公車改革深入推進。行業協會商會與行政機關脫鉤改革第二批試點啟動實施。加快不動產統一登記制度落地,全國100%的地(市、州)、98%的縣(市、區)實現“發新停舊”。國家科技計劃管理改革繼續深化,以增加知識價值為導向的分配政策出臺,科技成果轉化力度加大。教育領域綜合改革向縱深推進。分級診療制度建設持續推進,城鄉居民基本醫療保險制度整合取得實質性進展,個人衛生支出占衛生總費用的比重下降到28.9%。《國務院辦公廳關于全面放開養老服務市場提升養老服務質量的若干意見》(國辦發〔2016〕91號)印發實施。穩步推進機關事業單位養老保險制度改革。加快構建中國特色哲學社會科學,實施哲學社會科學創新工程。足球改革加快推進。 | 7) Social reforms were accelerated. Reform of the system for the use of official vehicles was completed in all organs of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council and its implementation was deepened in local Party and government bodies. A second group of trials to delink industry associations and chambers of commerce from the government were launched. Implementation of a unified registration system for immovable property was accelerated, with 100% of prefectures, prefecture-level cities, and autonomous prefectures and 98% of counties, county-level cities, and districts across the country issuing new certificates to replace old ones. Management reform for state science and technology initiatives was deepened, profit distribution policies were developed with the goal of strengthening the value ascribed to knowledge, and efforts to apply scientific and technological advances were intensified. Comprehensive education reform was stepped up. The system of tiered diagnosis and treatment was further developed, and substantive progress was made in integrating the basic medical insurance schemes for rural and non-working urban residents. The proportion of health care expenses borne by individuals dropped to 28.9%. Guidelines on Fully Opening up the Elderly Care Market and Improving Elderly Care Services (G.B.F. [2016] No. 91) by the State Council's General Office were published and implemented. We made steady progress in reforming the pension system for employees of Party and government offices and public institutions. We moved faster to develop philosophy and the social sciences with Chinese characteristics, and launched an initiative to encourage innovation in philosophy and the social sciences. We worked to speed up implementation of soccer reforms. |
專欄6:社會領域改革 新華社發 | Box 6: Social Reforms |
| 八是以“一帶一路”建設為統領推動開放型經濟水平不斷提升。“一帶一路”建設進展快速。“六廊六路多國多港”主骨架建設穩步推進,戰略對接、規劃對接成效顯著,中歐班列實現了統一品牌,累計開行近3000列。一批國際產能合作標志性工程落地,亞的斯亞貝巴-吉布提鐵路正式通車,從投融資、技術標準到運營管理維護,全部采用中國標準,標志著中國鐵路首次實現全產業鏈“走出去”。印尼雅萬高鐵、中老鐵路、中泰鐵路、馬來西亞南部鐵路、匈塞鐵路、瓜達爾港等重大項目有序推進。外商投資便利化程度進一步提高,非金融類實際使用外資保持穩定。對外投資管理體制機制更加完善,非金融類對外投資繼續增長。國際貿易“單一窗口”在沿海口岸全部啟用,通關一體化、檢驗檢疫一體化管理覆蓋全國。全年貨物貿易進出口總額下降0.9%,降幅比上年收窄6.1個百分點。服務貿易較快增長。人民幣正式加入國際貨幣基金組織特別提款權(SDR)貨幣籃子。特別是成功主辦二十國集團領導人杭州峰會,影響深遠。 | 8) The Belt and Road Initiative served as pacesetter to an open economy that saw continuous improvement. The Belt and Road (the Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st Century Maritime Silk Road) Initiative saw rapid progress. Development of the Initiative's framework, which consists of six corridors and six channels serving multiple countries and ports*, made steady progress, enabling China and its partners to markedly increase cohesion between their development strategies and plans. China-Europe freight train services, which have registered a total of nearly 3,000 trips, were brought under a single unified brand. A number of signature projects for international industrial-capacity cooperation got off the ground. The Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway officially came into service-from investment and financing to technology, operation, and management and maintenance, Chinese standards were applied throughout the project, making it the first full-production-chain export of China's railway. Steady progress was achieved in the construction of major international projects including railways connecting Jakarta and Bandung (high-speed railway), China and Laos, China and Thailand, and Hungary and Serbia; the railway project in southern Malaysia; and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan. Further steps were taken to facilitate foreign investment, ensuring that utilized non-financial foreign investment remained stable. The regulation system and institutions for outbound investment were improved, which enabled further growth of outbound non-financial investment. All coastal ports installed and started using the Single Window System for foreign trade, and all ports throughout China successfully integrated customs clearance procedures and inspection and quarantine procedures.China experienced a 0.9% fall in total imports and exports for the year, which was 6.1 percentage points less than the previous year's decrease. Trade in services grew rapidly. The RMB was officially included in the International Monetary Fund's special drawing rights (SDR) basket. Of particular note was China's hosting of the G20 2016 Hangzhou Summit which produced important and far-reaching outcomes. * The six corridors refer to economic corridors, comprising the New Eurasian Continental Bridge, the China-Mongolia-Russia corridor, the China-Central Asia-West Asia corridor, the China-Indochina Peninsula corridor, the China-Pakistan corridor, and the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar corridor. The six channels refer to communications and distribution channels comprising highways, railways, airlines, waterways, pipelines, and information networks. |
專欄7:重點開發開放功能平臺建設 新華社發 | Box 7: Major Platforms for Development and Opening up |
| (四)深入實施創新驅動發展戰略,經濟發展新動能加快成長。《國家創新驅動發展戰略綱要》印發實施,取得一批重大科技成果,高技術產業、裝備制造業、戰略性新興產業較快增長,創新對發展的支撐作用增強。 | 4. We deepened implementation of the innovation-driven development strategy, spurring the growth of new drivers for economic development. The National Strategy for Innovation-Driven Development was published and implemented. With a number of major scientific and technological advances as well as rapid growth in high-tech industries, equipment manufacturing, and strategic emerging industries, innovation has played an increasingly important role in bolstering development. |
| 一是創新能力持續提升。由點及面、有序布局重大科技創新平臺建設,深入推進8個區域全面創新改革試驗。北京、上海建設科技創新中心邁出新步伐。河北·京南、浙江、寧波3個國家科技成果轉移轉化示范區啟動建設。首個國家高速列車技術創新中心建成。完全自主知識產權中國標準高速列車正式投入運營。建成世界最大單口徑射電望遠鏡(FAST)等一批重大科技基礎設施,在量子通信、航空航天等方面取得一批重大科技成果。國家科技重大專項深入實施,科技創新2030-重大項目遴選確定。大力推動企業技術創新,落實好研發費用加計扣除、股權激勵和技術入股所得稅優惠、完善高新技術企業認定辦法等政策。 | 1) Innovation capacity continued to improve. We ensured the progressive and orderly development of major science and technology innovation platforms, and deepened pilot reforms on all-around innovation in eight regions. New strides were made in setting up science and technology innovation centers in Beijing and Shanghai. Work began to establish three national demonstration zones for the transfer and commercialization of scientific and technological achievements in Hebei-southern Beijing, Zhejiang, and Ningbo. The first national technology innovation center for high-speed trains was established, and the first Chinese-standard high-speed trains for which we hold complete intellectual property rights went into service. A number of major science and technology infrastructure projects were completed such as the project to build the world's largest single-aperture radio telescope, the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST). A number of significant scientific and technological advances were achieved in sectors including quantum communications, space, and aviation. We pressed ahead with implementing major national science and technology programs, and identified major projects for the Sci-Tech Innovation 2030 Agenda. A big push was made to encourage technological innovation among enterprises, with policies being implemented in relation to extra tax deductions for R&D costs, equity-based incentives for undertaking innovation, income tax incentives for personnel who contribute their technological achievements to become company shareholders, and improvements in the methods for defining new- and high-tech enterprises. |
| 專欄8:創新平臺建設 新華社發 | Box 8: Major Science and Technology Innovation Platforms |
| 二是大眾創業萬眾創新廣泛開展。28個國家雙創示范基地建設全面推進。雙創政策信息服務平臺開通,雙創白皮書發布。國家新興產業創業投資引導基金、科技成果轉化引導基金子基金和國家中小企業發展基金實體基金設立運行,投貸聯動試點啟動,創業擔保貸款創新發展。第二屆全國雙創活動周及“創響中國”巡回接力活動成功舉辦。大型央企建設雙創實體平臺128個,印發實施進一步完善中央財政科研項目資金管理等政策的若干意見,科研院所和高校鼓勵創新創業機制逐步完善,各類孵化器、專業化眾創空間日趨成熟。全年平均每天新登記企業1.51萬戶。 | 2) Entrepreneurship and innovation initiatives were carried out across the board. Work on establishing 28 national entrepreneurship and innovation demonstration centers moved forward on all fronts. Information service platforms for entrepreneurship and innovation policies began operating, and a whitepaper on entrepreneurship and innovation was published. The national seed fund for investing in emerging industries, the sub-funds of the seed fund for encouraging the application of scientific and technological advances, and the National SME Development Fund all came into operation. Trials got underway to allow banks to make combined debt-equity investments in startups and small businesses, and creative improvements were made to the system of guaranteed loans for business startups. The second National Week for Entrepreneurship and Innovation and the Innovating China Tour were a tremendous success. 128 platforms for entrepreneurship and innovation were developed by large-scale central government enterprises, guidelines on further improving the policies for managing the funding of central government-funded research programs were published and implemented, and mechanisms for encouraging entrepreneurship and innovation were gradually improved in research institutes and universities. All types of incubators and professional maker spaces saw continuous development. On average, 15,100 new enterprises were registered each day in 2016. |
| 三是新技術新產業新業態新模式蓬勃發展。工業機器人、集成電路、衛星應用、通用航空、生物等新產業快速發展。戰略性新興產業實現平穩增長,2016年,27個重點監測戰略性新興產業行業規模以上企業實現收入和利潤分別增長11.32%和13.96%。“互聯網+”行動和國家大數據戰略深入推進,人工智能、虛擬現實、基因工程等新技術加速興起,平臺經濟、分享經濟、協同經濟等新模式廣泛滲透,線上線下融合、跨境電商、社交電商、智慧家庭、智能交通等新業態不斷涌現。全年網上零售交易額近5.2萬億元,同比增長26.2%;其中,實物商品網上零售額占社會消費品零售總額的12.6%。 | 3) New technologies and industries as well as new forms and models of business flourished. There was rapid development in industrial robotics, integrated circuits, satellite applications, general aviation, bio-industry, and other new industries, while growth in strategic emerging industries was stable. In 2016, enterprises with annual turnover of 20 million yuan or more in 27 key strategic emerging industries increased their revenues by 11.32% and profits by 13.96%. We pressed ahead with implementing the Internet Plus initiative and the national big data strategy. Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, genetic engineering, and other new technologies experienced more rapid development. The platform, sharing, and collaborative economies, along with other new business models, achieved far-reaching penetration. New forms of business mushroomed, including combined online-offline businesses, cross-border and social networking e-commerce, smart home technology, and intelligent transportation. Online retail sales for 2016 reached nearly 5.2 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 26.2%, with online retail sales of goods accounting for 12.6% of total retail sales of consumer goods. |
| 四是傳統產業轉型升級步伐加快。加快落實《中國制造2025》,組織實施增強制造業核心競爭力三年行動計劃和制造業升級改造重大工程包,8個產業化實施方案順利推進。鐵路關鍵裝備研發試驗取得重大突破,226個智能制造綜合標準化試驗驗證和新模式應用項目有序開展,國家機器人檢測與評定中心建設進展順利。先進制造產業投資基金設立。 | 4) Transformation and upgrading of traditional industries accelerated. We moved faster to put the Made in China 2025 strategy into place, and organized implementation of the three-year action plan to enhance core competitiveness of our manufacturing industries and the project packages for transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing sector. The eight plans for industrial application were implemented smoothly. Major breakthroughs were made in research and development on key railway equipment. A total of 226 programs to run comprehensive, standardized tests on smart manufacturing technologies and apply new manufacturing models proceeded as planned. We made progress in building the National Robot Test and Evaluation Center. An investment fund for advanced manufacturing was set up. |
| 五是服務業創新發展穩步推進。落實加快發展生產性服務業、生活性服務業的兩個指導意見,服務業領域放寬市場準入實施規劃出臺,新一輪服務業綜合改革試點啟動。安排服務業發展引導資金,支持163個公共服務平臺建設。第三產業增速繼續超過第二產業,增加值占國內生產總值的比重提高到51.6%。 | 5) Solid steps were made in innovating and developing the service industry. We implemented the guidelines on accelerating the development of producer and consumer services and published the implementation plan for relaxing controls over market access in the service sector. A new round of comprehensive pilot reforms in the service sector began. We allocated funds for guiding the development of the service industry and supported the establishment of 163 public-service platforms. The tertiary industry has continued to outgrow the secondary industry, and the value-added of the tertiary industry accounted for a higher proportion of GDP, reaching 51.6%. |
| 六是基礎設施網絡進一步完善。加快推進現代綜合交通運輸體系建設,交通基礎設施網絡總里程突破500萬公里。交通提質增效、扶貧脫貧、重大基礎設施建設“一二三百”工程出臺實施,推進多式聯運發展,促進通用航空業發展,推動交通物流融合發展。能源生產和消費革命戰略出臺,能源供應能力不斷增強,非化石能源消費比重預計上升到13.3%,煤炭消費比重下降到62.0%。全國地級市基本建成光網城市,新一代信息基礎設施更加完善,建成全球最大的4G網絡。 | 6) Further improvements were made to infrastructure networks. As a result of accelerated development of the modern comprehensive transportation system, the length of transportation infrastructure networks open to traffic exceeded five million kilometers. We unveiled and implemented the 100 Demonstration Projects to Improve Transportation Quality and Efficiency, 200 Transportation Projects to Help Reduce Poverty, and 300 Major Transportation Infrastructure Projects. We worked to stimulate development of multimodal transportation and the general aviation industry and integrated the development of transportation and logistics infrastructure. The strategy on revolutionizing energy generation and consumption was launched, and energy supply capacity continued to grow stronger. The proportion of non-fossil energy consumption rose to an estimated 13.3% of total energy consumption while the proportion of coal consumption dropped to 62.0%. Fiber-optic networks were established in almost all prefecture-level cities, next-generation information infrastructure saw yet further enhancements, and China's 4G network, which is the world's largest, was completed. |
專欄9:重大基礎設施建設 新華社發 | Box 9: Major Infrastructure Construction |
| (五)著力提升農業可持續發展能力,農業現代化建設取得新進展。農業農村發展繼續保持穩中有進的良好態勢,糧食總產量達到6.16億噸,為經濟社會發展大局提供了有力支撐。 | 5. We worked to increase the capacity for sustainable agricultural development and achieved new progress in agricultural modernization. The trend of ensuring progress while maintaining stability continued in agricultural and rural development and grain output reached 616 million metric tons, thus ensuring agriculture served as a strong pillar of economic and social development. |
| 一是農業生產能力繼續提高。落實《全國新增1000億斤糧食生產能力規劃》,高標準農田建設加快推進,全面完成永久基本農田劃定,國家糧食安全和重要農產品供給保障能力進一步增強。新建糧食倉容195億斤。農業生產穩中調優,籽粒玉米種植面積調減2039萬畝,糧改飼、糧改豆試點范圍擴大,畜產品和水產品綜合生產能力繼續增強。農業綠色發展穩健起步,農業環境突出問題治理專項啟動實施,農業可持續發展試驗示范區啟動創建,“一控兩減三基本”行動取得階段性成效,對農業面源污染、東北黑土地、農牧交錯帶已墾草原綜合治理試點的支持力度加大。 | 1) Agricultural production capacity continued to increase. We implemented the plan to increase China's grain production capacity by 50 million metric tons, moved faster to develop high-quality farmland, and completed in full the work of designating permanent basic cropland throughout the country. As a result, our ability to guarantee national food security and the supply of major agricultural products has been further increased. New grain silos with a total capacity of 9.75 million metric tons were built. In working to optimize agricultural production while maintaining its stability, we reduced the area of land for corn kernel cultivation by 1.36 million hectares, expanded trials to cultivate feed crop or soybean crop instead of grain crop, and continued to raise overall production capacity for livestock and aquatic products. We made steady progress in promoting green agricultural development, launching a campaign to control and prevent serious agricultural environmental pollution, establishing pilot demonstration zones for sustainable agricultural development, and securing important achievements in implementing the action plan against pollution in rural areas*. We intensified support for trials to comprehensively manage agricultural pollution from non-point sources, chernozem soils in the northeast, and former grassland now under cultivation in transition areas between cropland and grassland. * The action plan aims to: 1) control water consumption for agricultural purposes; 2) cut the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers; 3) use recycling as a means of handling the pollution caused by the waste of livestock and poultry farming, plastic mulch film, and straw burning. |
| 二是農業農村基礎設施不斷完善。中小河流治理、小型病險水庫除險加固、灌排骨干工程建設與配套改造和小型農田水利建設等進展順利,新增高效節水灌溉面積2000萬畝以上,農村飲水安全鞏固提升工程啟動實施。新一輪農村電網改造升級工程,包括小城鎮中心村農網改造升級和平原地區農村機井通電等重點工程全面實施。農村交通基礎設施服務水平不斷提升,新改建農村公路29萬公里。“寬帶鄉村”工程繼續實施,電信普遍服務試點全面部署,農村信息基礎設施進一步改善。 | 2) Agricultural and rural infrastructure continued to improve. We successfully implemented projects to harness small and medium-sized rivers, reinforce small, dilapidated reservoirs, build key irrigation and drainage facilities as well as upgrade supporting infrastructure, and develop small-scale irrigation and water conservancy facilities. The area of cropland under efficient water-saving irrigation exceeded 1.33 million hectares. We also launched the project to consolidate and advance efforts to ensure safe drinking water in rural areas. A new round of power-grid improvement projects began throughout the country, including key projects for upgrading power grids in rural areas, small towns, and hub villages, and for providing power supply to all electric pump sets on rural flatlands. Transportation infrastructure and services in rural areas were continuously improved, and 290,000 kilometers of rural road were newly built or upgraded. We continued to implement broadband development projects in villages, carried out nationwide trials of providing universal telecommunications services in rural areas, and further improved rural information infrastructure. |
| 三是農村一二三產業融合發展進展順利。農村產業融合發展“百縣千鄉萬村”試點示范工程啟動,137個試點示范縣在優化發展布局、推進產城融合發展、構建現代農業產業體系、創新投融資機制等方面進行了積極探索。農村產業融合發展孵化園區加快建設,多元融合主體發展較快,打造了一批農業產業化龍頭企業,農村新產業新業態蓬勃發展。 | 3) Integrated development of the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries in rural areas advanced smoothly. The "100 counties, 1,000 townships, 10,000 villages" pilot demonstration project to promote rural industrial integration was implemented, with all 137 demonstration counties undertaking active explorations on how to improve development plans, promote integration between industrial development and urbanization initiatives, establish an industry system for modern agriculture, and innovate investment and financing mechanisms in the agricultural sector. We accelerated efforts to establish incubation parks for integrated development of industries in rural areas, develop diverse entities that integrate primary, secondary, and tertiary industry operations, and cultivate a group of leading enterprises in agricultural industrialization. New industries and new forms of business in rural areas experienced robust growth. |
| 四是農村改革穩步推進。農村土地所有權、承包權、經營權分置辦法出臺實施,土地承包經營權確權登記頒證面積超過8億畝。房地一體的農村宅基地、集體建設用地確權登記加快推進。農村集體產權制度改革意見出臺,農村集體資產股份權能改革試點和土地承包權有償退出試點積極開展。農村承包土地經營權和農民住房財產權抵押貸款試點穩妥有序推進。土地經營權流轉和抵押規模不斷擴大。各類新型經營主體發展壯大,數量超過270萬家。 | 4) Solid results were achieved in rural reform. We issued and implemented the Measures for Separating Land Ownership Rights, Contract Rights, and Management Rights in Rural Areas, and determined, registered, and certified contracted rural land-use rights for more than 53.3 million hectares of land. The determination and registration of integrated housing ownership and land-use rights for rural housing land and rights for collectively owned land designated for construction was accelerated. We drew up the Guidelines on Reforming the Rural Collective Property Rights System, and moved ahead with pilot reforms to grant shareholder rights for rural collective assets as well as trials to permit the sale of land contract rights. We carried out trials in a prudent and orderly fashion to allow rural residents to mortgage their contracted land-use rights and residential property rights. The cases of transferring or mortgaging rural land use rights have continually increased. New types of agribusinesses thrived and their number rose to more than 2.7 million. |
| (六)深入實施三大戰略和新型城鎮化,城鄉區域發展格局正在重塑優化。發揮三大戰略、“四大板塊”的疊加效應,促進城鄉區域協調協同發展,提升新型城鎮化質量和水平,新增長點增長極增長帶加快發展壯大。 | 6. We further implemented the Three Initiatives and New Urbanization, which has helped reshape and enhance the pattern of urban and rural development. We fostered synergy between the Three Initiatives (the Belt and Road Initiative, coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, and development of the Yangtze Economic Belt) and the coordinated development of the western, northeastern, central, and eastern regions. We promoted coordinated and integrated regional development and urban-rural development, and increased the quality and standards of New Urbanization. New growth areas, poles, and belts experienced stronger, faster development. |
| 一是三大戰略扎實有序推進。各省(區、市)主動融入絲綢之路經濟帶和21世紀海上絲綢之路建設,新疆、福建“一帶一路”核心區建設成效初顯。京津冀協同發展有序推進,北京城市副中心加快規劃建設,一批疏解示范項目穩步實施,交通、生態、產業三個重點領域協同推進,一批重大改革舉措落地。長江經濟帶發展規劃綱要印發實施,堅持共抓大保護、不搞大開發,綠色生態廊道建設加快推進,覆蓋上中下游地區的省際協商合作機制全面建立。 | 1) The Three Initiatives advanced in a solid and orderly manner. All provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government actively took part in the Belt and Road Initiative, and initial results were delivered in developing Xinjiang as the core of the Silk Road Economic Belt and Fujian as the core of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. In systematically promoting the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, we sped up planning and development of Beijing's sub-administrative center, implemented a number of demonstration projects to relieve Beijing of functions nonessential to its role as China's capital, facilitated coordination in three major areas-transportation, ecological conservation, and industrial development-and enacted a range of major reform measures. We published and implemented the Outline on Developing the Yangtze Economic Belt, continued coordinated efforts to champion environmental protection and eschew large-scale development, accelerated work on building a green, ecological corridor, and fully established a mechanism for inter-provincial consultation and cooperation covering the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the River. |
圖表5:“一帶一路”建設 新華社發 | Figure 5. The Belt and Road Initiative |
圖表6:京津冀協同發展 新華社發 | Figure 6. Coordinated Development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region |
圖表7:長江經濟帶發展 新華社發 | Figure 7. The Yangtze Economic Belt |
| 二是區域發展總體戰略和差別化區域政策深入實施。加快新一輪西部大開發,一批重大標志性工程開工建設,中西部地區經濟繼續保持較快增長。出臺實施新一輪東北振興戰略和若干重大政策舉措,國企改革、投資營商環境改善等重點領域改革取得新進展。明確中部地區“一中心、四區”重要戰略定位,長江中游城市群重要增長極作用強化。東部地區轉型升級、開放創新、陸海統籌優勢持續發揮,區域發展新動能新亮點不斷涌現。出臺促進區域協調發展的指導意見,差別化區域政策體系持續完善。國家綜合配套改革試驗區、國家級新區及各類開發區、承接產業轉移示范區、產城融合示范區、臨空經濟示范區等重要功能平臺建設有序推進。加快革命老區、民族地區、邊疆地區和集中連片特困地區脫貧攻堅。完善支持政策措施,推進新疆、西藏、四省藏區經濟社會發展和長治久安。 | 2) Implementation of the master strategy for regional development and differentiated development policies for different regions deepened. We increased efforts to accelerate large-scale development in the western region, with construction beginning on a number of signature projects. A relatively high-pace of economic development was maintained in the central and western regions. A new round of strategies and a number of major policies and measures for revitalizing the northeast were implemented, and reform in key areas, such as SOEs and the investment and business environment, made fresh progress. We underscored the strategic position of the central region, designating it as the country's key advanced manufacturing center, and as the priority area for New Urbanization, the core area for modern agricultural development, the demonstration area for promoting ecological progress, and the key area for comprehensive opening up. The city clusters along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River played a greater role as major growth poles. The eastern region continued to leverage its advantages in transforming and upgrading industries, in pursuing opening up and innovation, and in coordinating land and marine development to generate a constant stream of new drivers for growth and produce new highlights in development. We introduced guidelines on promoting coordinated development between regions, and continued to improve the system of differentiated regional policies. We ensured the orderly development of major function platforms-such platforms include national experimental zones for integrated, complete reform, state-level new areas and all types of development zones, demonstration zones for industrial relocation, demonstration zones for integrating industrial and urban development, and demonstration airport economic zones. We intensified efforts to combat poverty in old revolutionary base areas, areas with concentrations of ethnic minorities, border areas, and contiguous poor areas. We improved polices and measures for promoting economic and social development and continuing stability in Xinjiang, Tibet, and the Tibetan ethnic areas in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu, and Qinghai provinces. |
專欄10:“四大板塊” 新華社發 | Box 10: Development of the Four Regions |
| 三是新型城鎮化建設穩步推進。農業轉移人口市民化步伐加快,戶籍制度改革意見、居住證制度以及人地掛鉤、支持農業轉移人口市民化財政政策等關鍵性配套政策出臺,全年進城落戶人口達1600萬人,常住人口城鎮化率達到57.35%,戶籍人口城鎮化率達到41.2%。城市群規劃建設有序推進,支持武漢、鄭州建設國家中心城市。在全國開展新生中小城市和特色小(城)鎮培育,國家新型城鎮化綜合試點范圍擴大到2個省246個城市(鎮)。61個中小城市綜合改革試點取得積極成效。 | 3) We steadily advanced the development of New Urbanization. We granted urban residency to more people with rural household registration living in urban areas, and issued a number of key policies in support of this work, such as the guidelines on reform of the household registration system, the policy for implementing the residence certificate system,and the policy for linking increases in the amount of land designated for urban development in a locality to the number of former rural residents granted urban residency there. A total of 16 million people with rural household registration were granted urban residency in 2016. In total, permanent urban residents now account for 57.35% of the population, while the percentage of registered urban residents has reached 41.2%. We planned and developed city clusters in an orderly way, and supported Wuhan and Zhengzhou in developing as national principal cities. We facilitated the development of emerging small- and medium-sized cities as well as small towns with unique features across the country, and extended comprehensive trials of New Urbanization programs to two provinces and 246 cities and towns. Trials for comprehensive reform of small- and medium-sized cities yielded positive results in 61 cities. |
專欄11:新型城鎮化建設 新華社發 | Box 11: New Urbanization |
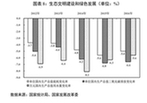
| (七)加強生態環境保護和能源資源節約,綠色發展初見成效。單位國內生產總值能耗和二氧化碳排放量分別下降5%和6.6%,超額完成全年目標,化學需氧量、氨氮、二氧化硫、氮氧化物排放量預計分別下降2.6%、2.9%、5.6%、4.0%,地級及以上城市空氣質量優良天數比例同比提高2.1個百分點,74個重點城市細顆粒物(PM2.5)年均濃度下降9.1%,地表水達到或好于Ⅲ類水體比例同比提高1.8個百分點、劣Ⅴ類水體比例同比下降1.1個百分點,萬元國內生產總值用水量下降5.6%。 | 7. We intensified environmental protection and energy and resource conservation, securing early achievements in promoting green development. Energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP fell by 5% and 6.6% respectively, both surpassing annual targets. According to estimated figures, chemical oxygen demand was reduced by 2.6%, ammonia nitrogen emissions by 2.9%, sulfur dioxide emissions by 5.6%, and nitrogen oxide emissions by 4.0%. A year-on-year increase of 2.1 percentage points occurred in the proportion of days with good or excellent air quality for cities at or above prefectural level, while the annual average PM2.5 concentrations in 74 key cities dropped by 9.1%. The proportion of surface water with a national quality rating of Grade III or above rose by 1.8 percentage points year on year, and the proportion of surface water with a rating lower than Grade V, meanwhile, fell by 1.1 percentage points. Water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP fell by 5.6%. |
圖表8:生態文明建設和綠色發展 新華社發 | Figure 8. Ecological Progress and Green Development |
| 一是生態文明建設取得新進展。生態文明建設目標評價考核辦法印發實施。決定在福建省、江西省和貴州省開展國家生態文明試驗區建設,生態文明先行示范區建設持續深化。健全國家自然資源資產管理體制試點方案、省以下環保機構監測監察執法垂直管理制度改革試點指導意見、控制污染物排放許可制實施方案、劃定并嚴守生態保護紅線若干意見、培育環境治理和生態保護市場主體意見等一批改革方案印發實施。在吉林等7省(市)開展生態環境損害賠償制度改革試點。全面推行河長制意見出臺。生態保護補償機制不斷健全。新一輪退耕還林還草、重點防護林、石漠化綜合治理、京津風沙源治理、水土流失綜合治理等工程加快推進,濕地保護體系初步形成。開展中央環境保護督察。 | 1) Work to promote ecological progress moved ahead. We promulgated and implemented the measures on evaluating performance in advancing ecological progress. We decided to build pilot zones for ecological advancement in Fujian, Jiangxi, and Guizhou provinces, and stepped up the development of pilot demonstration zones for promoting ecological progress. We issued and implemented a number of reform plans on ecological progress, including: the pilot plan on improving the national system for natural-resource asset management; the guidelines for trial reforms to establish a system to bring county- and prefecture-level environmental monitoring, inspection, and law enforcement bodies directly under the jurisdiction of provincial-level environmental bodies; the plan for implementing the emissions permit system to tighten emissions control; and the guidelines on establishing and holding firm to the red lines for ecological conservation and on fostering market entities for environmental governance and ecological conservation. Pilot reforms of the compensation system for ecological and environmental damage were carried out in seven provinces and municipalities directly under the central government including Jilin. The guidelines on bringing the river chief system into full operation were issued, and mechanisms for compensating ecological conservation efforts were improved. We moved faster to implement a new round of projects to return marginal farmland to forest and grassland, build key forest shelterbelts, comprehensively address the expansion of stony deserts, control the sources of dust storms affecting Beijing and Tianjin, and bring soil erosion under control. A basic framework for wetland conservation was put in place. The central government carried out environmental inspections. |
| 二是主體功能區戰略深入實施。國家重點生態功能區范圍拓展到676個縣及87個重點國有林區林業局,產業準入負面清單制度出臺實施。省級海洋主體功能區規劃編制實施工作在11個沿海省份展開。三江源、東北虎豹、大熊貓、神農架、武夷山、錢江源等國家公園體制試點方案印發實施。資源環境承載能力監測預警機制初步建立,先行在京津冀地區試點。市縣“多規合一”試點深入推進,省級空間規劃試點方案印發實施。全國國土規劃綱要、全國土地利用總體規劃綱要調整方案印發實施。 | 2) The development strategy for functional zones was further implemented. Key ecosystem service zones have been established in 676 counties and 87 forestry bureaus in key state forestry areas. A negative list for industry access to key ecosystem service zones was issued and put into force. Work got under way in 11 coastal provinces to draw up and implement plans for marine functional zones. The plan for establishing a national park system on a trial basis was implemented, with trials going ahead in national parks at the Yangtze, Yellow, and Lancang riversources, in the habitats of Siberian tigers, Far Eastern leopards, and giant pandas, in the Shennongjia area, in the Wuyi Mountains, and at the source of the Qiantang River. The mechanisms for monitoring and providing early warning on the carrying capacity of resources and the environment were basically established, with initial trials being implemented in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The pilot project for municipal or county-level governments to integrate various types of urban plans into a single urban plan moved forward, and the plan to carry out spatial-planning trials at the provincial level was implemented. The National Land Plan (2016-2030) and the Adjustments to the General Plan for National Land Use (2006-2020) were introduced. |
| 三是節能減排持續推進。“十二五”省級人民政府節能目標責任評價考核結果公布,“十三五”能耗、水耗總量和強度“雙控”制度建立實施,在浙江、福建、河南、四川4省開展用能權有償使用和交易制度試點。循環經濟發展加快,生產者責任延伸制度方案印發實施,產業園區循環化改造繼續推進。印發《“十三五”節能環保產業發展規劃》,構建綠色金融體系指導意見出臺實施,發行各類綠色債券2296.6億元,節能環保產業不斷做大做強。 | 3) Sustained progress was made in energy conservation and emissions reduction. The results of performance evaluations of provincial-level governments in fulfilling responsibilities for energy conservation targets during the 12th Five-Year Plan period were released to the public. The system to control both the total amount and intensity of energy and water consumption during the 13th Five-Year Plan period was established. Pilot projects to set up systems for the paid use and trade of energy consumption rights were carried out in Zhejiang, Fujian, Henan, and Sichuan provinces. We stepped up development of the circular economy, issuing the plan to create a system for extended producer responsibility and making strides in promoting circular operations within industrial parks. The plan for developing energy conservation and environmental protection industries during the 13th Five-Year Plan period was issued. The guidelines on establishing a green finance system were introduced and applied, bonds worth 229.66 billion yuan for launching eco-friendly initiatives were issued, and the energy conservation and environmental protection industries achieved robust growth in terms of both scale and strength. |
| 四是環境綜合治理力度加大。《京津冀地區大氣污染防治強化措施(2016-2017年)》發布實施,重點地區煤炭消費量進一步壓減,加快燃煤電廠超低排放改造,全國累計淘汰黃標車和老舊車404.6萬輛。制定實施2016-2017年長江經濟帶生態環境保護行動計劃,完成11省(市)126個地級及以上城市全部319個集中式飲用水水源保護區劃定,出臺《全國重要飲用水水源地名錄》,排查整治城市黑臭水體和非正規垃圾堆放點。深入開展農村生活垃圾治理專項行動,推進農村人居環境綜合整治。土壤污染防治行動計劃發布實施,出臺污染地塊土壤環境管理辦法,啟動14個土壤污染治理與修復試點項目和6個土壤污染綜合防治先行區建設,加強重金屬污染防控重點區域綜合治理。全國礦山地質環境恢復和綜合治理進一步加強。環境風險管控水平進一步提高,突發環境事件得到妥善處置。 | 4) More was done to comprehensively address environmental problems. Stronger measures on the prevention and control of air pollution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (2016-2017) were promulgated and implemented, and coal consumption in key areas was further cut. Coal-fired power plants were urged to swiftly upgrade their facilities and achieve ultra-low emissions. A total of 4.046 million old and high-emission vehicles were removed from roads nationwide. The action plan on environmental protection of the Yangtze Economic Belt (2016-2017) was implemented. Planning was completed on the establishment of protection zones for 319 centralized drinking water sources in 126 cities at or above prefectural level in 11 provinces and provincial-level municipalities. The national list of major drinking watersources was formulated. We identified and cleaned up both black, malodorous water bodies and undesignated refuse dumping points in urban areas. A project to manage household refuse in rural areas got fully under way, and comprehensive measures were taken to improve the rural living environments. We issued the action plan to prevent and control soil pollution and the measures for soil environmental governance on polluted land plots, launched 14 related pilot projects aimed at prevention, control, and restoration, and also established six trial zones for comprehensively preventing and curbing soil pollution. Greater efforts were taken to comprehensively improve land in key areas contaminated by heavy metals. We continued to improve and restore the geological environment in mining areas throughout the country. We made headway in managing and controlling environmental risks and in responding effectively to environmental emergencies. |
| 五是應對氣候變化工作不斷強化。“十三五”控制溫室氣體排放工作方案印發實施。低碳省市、城(鎮)、園區、社區等試點示范有序開展。碳排放權交易市場建設積極推進。城市適應氣候變化行動方案發布實施。氣候變化南南合作加快推進,“十百千”項目啟動實施。首批簽署和較早批準《巴黎協定》,創新性推動實現中美元首出席批準文書交存儀式,為推動《巴黎協定》盡早生效作出歷史性貢獻。建設性參加聯合國氣候變化馬拉喀什會議并推動會議取得成功。 | 5) Our efforts to respond to climate change grew stronger. A work plan to control greenhouse gas emissions during the 13th Five-Year Plan period was introduced. Trials and demonstrations to encourage low-carbon growth in provinces, municipalities, cities, towns, industrial parks, and communities proceeded in an orderly manner. Encouraging progress was made in establishing a national market for the trading of carbon emission rights. The Action Plan on Developing Climate Resilient Cities was promulgated. We quickened the pace of South-South cooperation on climate change and launched cooperation projects in developing countries to set up 10 low-carbon demonstration zones, launch 100 mitigation and adaption programs, and provide 1,000 places on climate-change training programs. China was one of the first countries to sign the Paris Climate Agreement and also ratified it at a relatively early stage. The presidents of China and the United States deposited with United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon their respective country's instrument to join the Paris Agreement-the proposal to hold the ceremony, which was the first of its kind, was put forward by China, making a significant contribution toward the early entry into force of the Paris Agreement. China attended the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Marrakech, Morocco, where it played a constructive role and contributed to the overall success of the conference. |
| (八)加快發展社會事業和改善民生,人民生活水平持續提升。全力推進精準扶貧精準脫貧,加強社會政策托底,努力提高基本公共服務均等化水平。 | 8. We moved faster to develop social programs and improve people's wellbeing, ensuring that living standards continued to rise. We directed major efforts toward implementing targeted measures for poverty alleviation and elimination, made social policies more effective in meeting basic living needs, and ensured more equitable access to basic public services. |
專欄12:精準扶貧精準脫貧工程 新華社發 | Box 12: Targeted Poverty Reduction Projects |
| 一是脫貧攻堅戰全面打響。《“十三五”脫貧攻堅規劃》發布實施,全國財政專項扶貧資金投入超過1000億元。印發實施“十三五”易地扶貧搬遷規劃,22個省(區、市)全面啟動易地扶貧搬遷項目,全年249萬人易地扶貧搬遷建設任務如期完成。金融扶貧、特色產業扶貧、教育扶貧、交通扶貧、水利扶貧、旅游扶貧、光伏扶貧、電商扶貧、以工代賑等深入推進。東西部扶貧協作不斷深化。推動集中連片特困地區“十三五”省級實施規劃落地,對川陜等革命老區、贛南等原中央蘇區振興發展與脫貧攻堅支持力度持續加大。支持四川涼山、云南怒江、甘肅臨夏等面臨特殊困難的少數民族自治州加快建設小康社會進程。 | 1) The fight against poverty began in full swing. The plan for poverty elimination during the 13th Five-Year Plan period was released and implemented, and over 100 billion yuan was allocated to government poverty-alleviation funds nationwide. The plan for relocating people from inhospitable areas during the 13th Five-Year Plan period was published and implemented. In line with this, related projects were launched in 22 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government, and last year's objective to provide housing for the 2.49 million people relocated from inhospitable areas was completed on time. We made great progress in reducing poverty by providing financial support and by promoting the development of locally viable industries, education, transportation, water conservancy projects, tourism, photovoltaic power facilities, e-commerce, and work-relief programs in poor areas. Coordination on poverty reduction between the western and eastern regions continued to grow. We worked to ensure the implementation of the provincial plan for promoting development and fighting poverty in contiguous poor areas during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. Greater support was given to promote revitalization and development and to reduce poverty in old revolutionary base areas such as the Sichuan-Shaanxi region and the former Central Soviet Area in southern Jiangxi. We supported extremely poor autonomous prefectures with concentrations of ethnic minorities, such as Liangshan in Sichuan, Nujiang in Yunnan, and Linxia in Gansu, to ensure they can work more quickly in building a moderately prosperous society. |
| 二是社會保障能力不斷加強。全國居民人均可支配收入實際增長6.3%,農村居民收入增幅連續7年高于城鎮居民。退休人員基本養老金水平提高6.5%左右。基本醫療保險參保人數超過13億,城鄉居民基本醫保補助標準由每人每年380元提高到420元。在全國范圍內建立了困難殘疾人生活補貼和重度殘疾人護理補貼制度。 | 2) The capacity to provide social security was constantly enhanced. Per capita disposable personal income increased by 6.3% in real terms, and the growth rate of rural income was greater than that of urban income for the seventh year in a row. Basic pension benefits for retirees were raised by approximately 6.5%. The number of people under the basic medical insurance system exceeded 1.3 billion, and the government subsidy for basic medical insurance for rural and non-working urban residents increased from 380 yuan to 420 yuan per capita per annum. The system for granting living allowances to people with disabilities who face financial difficulties and providing a care subsidy to people with serious disabilities was put in place across the country. |
| 三是公共服務供給持續改善。學前教育毛入園率、九年義務教育鞏固率、高中階段毛入學率分別達到77.4%、93.4%和87.5%。高等教育毛入學率達到42.7%,超過中高收入國家平均水平。現代職業教育體系進一步完善和發展。城鄉基本醫療服務體系進一步健全,基本公共衛生服務項目年人均財政補助達到45元,均等化水平明顯提高。“健康中國2030”規劃綱要發布實施,每千人口執業(助理)醫師數增長到2.31人,每萬人全科醫生數增長到1.53人。全年出生人口達到1786萬人,全面兩孩政策平穩落地,生育服務保障進一步加強。公共文化服務體系建設繼續加強,各省(區、市)均已出臺本地區的基本公共文化服務實施標準。實施中華優秀傳統文化傳承發展工程的意見等基礎性制度出臺。實施全民健身計劃,體育健兒在里約奧運會、殘奧會上再創佳績。冰雪、水上、航空、山地戶外等運動加快發展。 | 3) The supply of better public services was maintained. The gross enrollment ratio for preschool education came to 77.4%; the retention rate of nine-year compulsory education grew to 93.4%; and the gross enrollment ratio for senior secondary education reached 87.5%. The gross enrollment ratio for higher education stood at 42.7%, surpassing the average level of upper-middle-income countries. The modern vocational education system was further improved. The system for providing basic medical care services for rural and urban residents also improved and the government subsidy for basic public health services increased to 45 yuan per capita per annum, helping to make access to services far more equitable. The Healthy China 2030 Program was issued and implemented. The number of occupational physicians and physician assistants increased to 2.31 per 1,000 people and the number of general practitioners grew to 1.53 per 10,000 people. We ensured smooth implementation of the policy to allow couples to have two children and further improved childbirth services; and China celebrated the births of 17.86 million babies over the course of the year. The system of public cultural services was further strengthened and all provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the central government worked out standards for providing these services. The basic elements underlying the project to develop and pass on fine Chinese cultural traditions, such as the implementation guidelines, were formulated. The Fitness for All initiative was launched, and Chinese athletes once again achieved great success at the Olympic and Paralympic Games which were held in Rio de Janeiro. Winter, water, and aviation sports, mountaineering and outdoor pursuits, as well as other sports all developed at a faster pace. |
專欄13:公共服務供給 新華社發 | Box 13: Supply of Public Services |
| 四是保障性安居工程建設扎實推進。加大中央預算內投資和中央財政專項資金支持力度,繼續發揮企業債券直接融資作用,支持棚戶區住房改造等保障性安居工程。2016年,完成棚戶區住房改造600多萬套,農村危房改造380多萬戶。 | 4) The construction of government-subsidized housing progressed steadily. We supported government-subsidized housing projects, such as the rebuilding of run-down areas, by increasing central government budgetary investment and special funding in this area and continuing to secure direct financing through corporate bond issuance. In 2016, we rebuilt over six million housing units in run-down urban areas and renovated over 3.8 million dilapidated rural houses. |
| 從計劃指標運行情況看,經濟增長、就業、價格總水平、國際收支平衡等主要指標保持在合理區間,科技創新、生態環保、民生保障等反映發展質量和效益的指標進一步改善,總的完成情況是好的。 | In assessing the overall situation related to the targets set out in the 2016 Plan, we can see that major targets for national and social development, such as the economic growth rate, employment levels, the consumer price index, and the balance of payments, were kept within proper range. While our performance in relation to targets reflecting the quality and benefits of development, such as those concerning scientific and technological innovation, ecological conservation and environmental protection, and people's wellbeing, was further improved. Overall, the 2016 Plan was successfully implemented. |
| 19個約束性指標全部完成。43個預期性指標中,38個指標運行情況符合或高于預期,第一產業、全社會固定資產投資、貨物進出口額、廣義貨幣供應量(M2)增長率、城鎮居民人均可支配收入5個指標運行值與預期值存在差距。需要說明的是,預期性指標的計劃目標不是指令性的,也不是預測值,而是國家期望的發展目標,體現預期和政策導向,實際運行情況可能高于預期目標,也可能低于預期目標。部分指標運行值與預期目標存在差距,主要有以下原因:一是針對農產品階段性供大于求、庫存高企、價格低迷的形勢,主動推進種養結構調整,部分主要農產品產量有所回落,因此第一產業增加值增幅略低于預期目標。二是受市場需求偏弱、投資回報下降、企業信心不強等因素綜合影響,投資特別是民間投資、制造業投資下行壓力較大,加上固定資產投資價格下跌持續時間和幅度超出預期,導致全社會固定資產投資增幅低于預期目標。三是受全球經濟復蘇乏力、國際貿易需求疲軟、針對我國的保護主義加劇等影響,貨物貿易進出口雖回穩向好,但仍難以實現預期目標。四是為供給側結構性改革營造適宜的貨幣金融環境,在對實體經濟提供足夠支持的同時,貨幣供應切實體現了不搞“大水漫灌”和去杠桿、防風險、抑制資產價格泡沫的要求,因此廣義貨幣供應量(M2)增速低于預期目標。五是從收入指標完成情況看,全國居民人均可支配收入增長與經濟增長基本同步,受經濟下行壓力影響,部分行業從業人員工資性收入增幅放緩,導致城鎮居民人均可支配收入增幅低于預期目標。 | All 19 obligatory targets were achieved as planned. Of the 43 anticipatory targets, 38 were either on target or exceeded, while performance in relation to the remaining five-targets for the primary industry, fixed-asset investment, the total import and export volume of goods, M2 money supply growth rate, and per capita disposable income of urban residents-fell short of expectations. It should be clarified that the anticipatory targets are neither mandatory nor predicted; as development objectives that the government hopes to meet, they are a reflection of the anticipated direction of national development and policy orientation. The actual performance for these targets may be higher or lower than the planned figures. The major reasons for the discrepancies between the projected figures for these anticipatory targets and actual performance are as follows: First, to deal with a period of supply in agricultural products outstripping demand as well as a build-up in the inventory of agricultural products and a resulting trend of depressed prices, we took the initiative to adjust what and how much we grow and breed, which caused the output of some major agricultural products to drop off. As a result, the increase in the value-added of the primary industry was slightly lower than the planned figure. Second, a combination of insufficient market demand, a decrease in returns on investment, and low confidence among enterprises gave rise to considerable downward pressure on investment, particularly investment from private sources and in the manufacturing sector. These factors, as well as a prolonged and larger-than-expected drop in fixed-asset investment prices resulted in the increase in fixed-asset investment being lower than the anticipatory target. Third, a range of factors, such as a stuttering global economic recovery, weak demand in the international trade market, and increasing protectionism against China, meant that, although the total import and export volume of goods began to rise steadily, it still fell short of projected figure. Fourth, we needed to ensure that a favorable monetary and financial environment for supply-side structural reform was created. So while ensuring there was sufficient support in place for the real economy, we stayed away from strong stimulus policies affecting money supply that would have an economy-wide impact, and instead worked to deleverage, guard against risks, and prevent an asset price bubble. As a result, the growth rate of M2 money supply fell short of projected figure. Fifth, in assessing the situation in relation to targets regarding income, we see that increases in per capita disposable personal income stayed basically in step with economic growth. The influence of downward pressure on the economy, however, caused the growth of salary-based incomes for employees in certain industries to slacken. As a result, increase in urban per capita disposable income fell short of the planned figure. |
| 總之,在國內外形勢錯綜復雜的情況下,我國經濟增速繼續走在世界前列,發展質量和效益提高,經濟結構繼續優化,人民生活水平持續改善,生態環境有所好轉,成績來之不易。這是黨中央、國務院正確領導的結果,是各地區各部門共同努力的結果,是全國各族人民團結奮斗的結果。 | To sum up, despite complex situations both at home and abroad, we still made considerable achievements-our country's economic growth rate was still faster than most countries in the world; the quality and efficacy of development grew; the economic structure was further improved; increases in living standards were sustained; and ecosystems and the environment also saw some improvement. These achievements have not come easily. They are a result of the correct leadership of the Party Central Committee and the State Council, the collective hard work of all regions and departments,and the concerted efforts of the people of all our ethnic groups. |
| 同時,我們也清醒地認識到,世界經濟仍然在深度調整,復蘇動力不足,不穩定和不確定性將進一步凸顯,國際投資和貿易低迷,保護主義、內顧傾向抬頭。國內經濟穩定運行的基礎還不牢固,仍面臨不少突出矛盾和問題。一是實體經濟結構性供需失衡。供給體系產能大多數只能滿足中低端、低質量、低價格的需求,隨著消費結構加快升級,出口需求和投資需求相對下降,供給結構不適應需求新變化。二是有效需求增長乏力。有效投資特別是民間投資、制造業投資增速較低。經濟下行對就業、收入、消費的滯后影響開始顯現。國際需求持續低迷,國內綜合要素成本不斷上漲,產業和訂單向外轉移加快,我國外貿發展面臨的形勢更加復雜嚴峻。三是部分區域、行業、企業困難較大。一些資源型和傳統產業比重大的地區,下行壓力和發展困難較大。部分行業分化調整的影響,可能沿產業鏈傳導。受市場環境偏緊和經營成本較高雙重擠壓,企業盈利能力較弱、虧損面較大。四是部分領域風險仍在積累。一些地區財政收支矛盾突出,防控金融風險力度需進一步加大,房地產市場仍面臨結構性高房價、高庫存雙重挑戰。五是大氣霧霾等環境問題仍然突出。多頻次、廣區域、長時間、重濃度的霧霾天氣,給人民生產生活帶來較大影響。與此同時,安全生產、食品藥品質量和民生等領域也出現一些新問題。我們要高度重視,準確分析研判國內外形勢,增強憂患意識,強化底線思維,保持戰略定力,更加有效應對。 | While recognizing our achievements, we are also keenly aware that the world economy is still undergoing profound adjustment and that impetus for economic recovery is lacking, instabilities and uncertainties are increasing, international investment and trade are inadequate, and protectionism and other inward-looking trends are on the rise. China's economy is still without a solid enough foundation for ensuring steady development and still faces a number of acute problems. First, the real economy is beset by a structural imbalance between supply and demand. The majority of production capacity within the supply system can only meet demand for products that are at the middle-to-low end or are of a low price or poor quality. Upgrading within the consumption structure is occurring at an increasingly faster pace; by contrast, export and investment demand are decreasing. These new changes in demand are something that the supply structure has yet to properly adapt to. Second, growth in effective demand is weak. Effective investment is growing slowly, particularly investment from private sources and in manufacturing. The delayed impact of downward economic pressure on employment, income, and consumption is now starting to show. The increasingly complex and challenging situation relating to China's foreign trade development is marked by persistently weak international demand, rising costs for multiple factors of production at home, and an increase in the pace at which industries and orders for goods are shifting to other countries. Third, some regions, industries, and enterprises are confronted with serious difficulties. Resource-dependent areas and strongholds of traditional industry are experiencing severe downward pressure and great difficulties in development. There is a possibility that the effects of divergent growth trends and adjustments, which some industries are experiencing, will end up being transmitted throughout the industry chain. Having been pressed by insufficient market demand and comparatively high operational costs, the ability of enterprises to make a profit has decreased and a greater number of enterprises are suffering losses. Fourth, risks are mounting in some sectors. Notable imbalances exist between government revenue and expenditures in some localities; greater efforts need to be made to guard against and control financial risks; and the real estate market is still facing serious structural challenges on two fronts, with exorbitant housing prices in some cities and overabundant inventory in others. Fifth, environmental problems such as smog are still grave. Frequent and prolonged periods of heavy smog extending across large areas have greatly affected the work and lives of our people. At the same time, new problems in relation to workplace safety, food and medicine quality, and the people's wellbeing are also emerging. We must give top priority to these issues, carry out studies and analysis to correctly assess the domestic and international situations, increase our awareness of potential dangers and of the lines that are not to be crossed, and maintain strategic resolve so as to ensure we produce a more effective response. |
 0
0 



![3月5日,第十二屆全國人民代表大會第五次會議在北京人民大會堂開幕。 [新華社] 3月5日,第十二屆全國人民代表大會第五次會議在北京人民大會堂開幕。 [新華社]](http://images.china.cn/site1007/2017-03/20/b8aeed9904561a3980ac1a.jpg)